Best Practice: Use Component Architectures
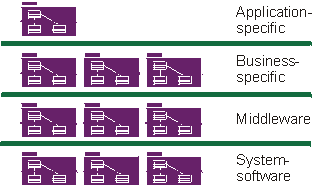
Component-based
architecture with layers
Topics
Components are cohesive groups of code, in source or executable form, with
well-defined interfaces and behaviors that provide strong encapsulation of
their contents, and are, therefore, replaceable. Architectures based around components
tend to reduce the effective size and complexity of the solution, and so are more
robust and resilient.
Use cases drive the Rational Unified Process (RUP) end-to-end over the whole
lifecycle, but the design activities are centered around the notion of system
architecture
and, for software-intensive systems, software architecture.
The main focus of the early iterations of the process—mostly in the
elaboration phase—is to produce and validate a software
architecture, which in the initial development cycle takes the form
of an executable architectural prototype that gradually evolves to become the
final system in later iterations.
By executable architecture, we mean a
partial implementation of the system built to demonstrate selected system
functions and properties, in particular those satisfying non-functional
requirements. The purpose of executable architecture is to mitigate risks related to performance, throughput,
capacity, reliability, and other "ilities", so that the complete functional
capability of the system may be added in the construction
phase on a solid foundation, without fear of breakage.
For an introduction to the notion of architecture—most specifically
software architecture—and an explanation of why this notion is crucial, see Concepts:
Software Architecture.
The RUP provides a methodical, systematic way to
design, develop, and validate an architecture. We offer templates for
architectural description around the concepts of multiple architectural
views, and for the capture of architectural style, design rules, and constraints.
The Analysis
and Design discipline contains specific activities aimed at identifying
architectural constraints and architecturally significant elements, as
well as guidelines on how to make architectural choices. The management
process shows how the planning of the early iterations takes into account
the design of an architecture and the resolution of the major technical
risks. See the Project Management
discipline and all activities associated with the Role:
Software Architect for further information.
Architecture is important for several reasons:
- It lets you gain and retain intellectual control over the project, to
manage its complexity and to maintain system integrity.
A complex system is more than the sum of its parts; more than a succession of
small independent tactical decisions. It must have some unifying, coherent
structure to organize those parts systematically and it must provide precise rules on
how to grow the system without having its complexity "explode" beyond
human understanding.
The architecture establishes the means for improved communication and
understanding throughout the project by establishing a common set of references,
a common vocabulary with which to discuss design issues.
- It is an effective basis for large-scale reuse.
By clearly articulating the major components and the critical interfaces
between them, an architecture lets you reason about reuse—both internal reuse,
which is the identification of common parts, and external reuse, which is the incorporation of
ready-made, off-the-shelf components. However, it also allows reuse on a larger
scale: the reuse of the architecture itself in the context of a line of products
that addresses different functionality in a common domain.
- It provides a basis for project management.
Planning and staffing are organized along the lines of major components.
Fundamental structural decisions are taken by a small, cohesive architecture
team; they are not distributed. Development is partitioned across a set of small
teams, each responsible for one or several parts of the system.
A software component can be defined as a nontrivial piece of software, a
module, a package, or a subsystem, all of which fulfill a clear function, have a clear
boundary, and can be integrated in a well-defined architecture. It's the
physical realization of an abstraction in your design.
Components come from different places:
- In defining a very modular architecture, you identify, isolate, design,
develop, and test well-formed components. These components can be
individually tested and gradually integrated to form the whole system.
- Furthermore, some of these components can be developed to be reusable,
especially the components that provide common solutions to a wide range of
common problems. These reusable components, which may be larger than just
collections of utilities or class libraries, form the basis of reuse within
an organization, increasing overall software productivity and quality.
- More recently, the advent of commercially successful, component
infrastructures—such as CORBA, the Internet, ActiveX, and JavaBeans—trigger
a whole industry of off-the-shelf components for various domains, allowing
you to buy and integrate components rather than developing them all
in-house.
The first point in the preceding list exploits the old concepts of modularity and encapsulation,
bringing those concepts underlying object-oriented technology a step further. The
last two points in the list shift software development from programming software
a line at time, to composing software by assembling components.
The
RUP supports component-based development in these ways:
- The iterative approach allows you to progressively identify components,
and decide which ones to develop, which ones to reuse, and which ones to buy.
- The focus on software architecture allows you to articulate the structure—the components and the ways in which they
integrate—which include the fundamental
mechanisms and patterns by which they interact.
- Concepts, such as packages, subsystems, and layers, are used during
Analysis
& Design to organize components and to specify interfaces.
- Testing is first organized around components, then gradually around larger sets
of integrated components.
Copyright
© 1987 - 2001 Rational Software Corporation
| |
|
 Overview >
Overview >
 Best Practices >
Best Practices >
 Use Component Architectures
Use Component Architectures
 Overview >
Overview >
 Best Practices >
Best Practices >
 Use Component Architectures
Use Component Architectures