

This lesson presents the philosophy, objectives, techniques and tools concerning the activities and duties of a Test Manager or Test Engineer during the formal test phases. The four formal test phases are function, system, installation and acceptance. Each of the four test phases will be discussed with regard to the activities, regression tests, entry criteria, entry inputs, exit criteria and, exit output.
The philosophy for formal testing is based on the premise that if the test engineer is looking for defects they will find them. The test engineer is less biased and has a separate interpretation of the software than the software engineer who developed the software. Formal indicates that test engineering is an independent team and the team prepares the detailed test documentation to formally document test activities. Whereas informal testing is performed by the software engineering (unit & integration test) and is not meant to imply that there is not a process in place for these types of tests.
Formal testing is a repeatable process. The repeatability in the test effort is achieved by documenting all test work artifacts. The test cases are especially documented so that the identical test can be rerun. Formal Test concentrates on verifying that Software Requirements Specifications are met for the CSCI’s, therefore the test engineering must be able to show traceability from requirements specification into test documentation. Software configuration management load build, means that the formal test is being conducted on controlled code under configuration management. Black box testing is performed during formal testing. This is in contrast to white-box testing. Formal testing is based on the requirements and not on the implementation of the requirements.
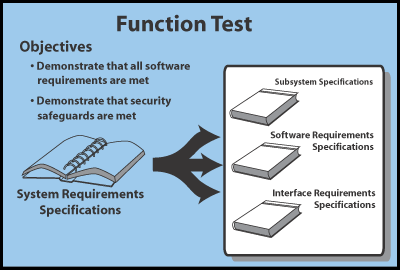
Function testFunction test is equivalent to Formal Qualification Test (FQT) using the Government MIL-STD-2167A terminology. Function test concentrates on demonstrating that all software requirements are met. The Figure Function Test illustrates that the system requirements specification (there may be multiple documents specifying the system-level requirements) is analyzed and the software requirements are mapped into software specifications and interface specifications. From this set of documentation the function test specification document draws its requirements. The test plans are then drawn form the test specification document. For systems with security-related requirements, functional tests are performed to insure security safeguards are met.
The following function test techniques are a few examples of the types of techniques that are applicable to function (black-box) testing. The descriptions for these tests were defined in previous lessons. The test techniques are:
- Equivalence partitioning
- Boundary condition testing
- Database
- Input validation & syntax checking
- State transition
- Transaction flow
The function test tools for the test engineer to consider are:
- Capture or replay tool
- Test case manager
- Data reduction
- Defect tracking
The function test activities were described in the previous lesson but will be reiterated. The activities are:
- Test Execution
- Logging problems detected
- Retest resolved problems
- Obtain witness signatures
- Regression test
Regression test was not discussed in the previous lesson and is the final set of activities within the function test. The regression test activities also follow each of the next three formal tests. The objective of regression test is to ensure that no problems have been introduced into the system as a result of the change process. The use of the word system refers to both software and hardware components being delivered. The change process implies the problems resolved by problem reports and, enhancements by engineering change proposals or requests. If test engineering is using a capture or replay tool for testing and the test cases needs to be witnessed by the client (QA or security), test engineering will need to arrange for the witnesses to verify each step and the expected results from the automated output report.
Scope of regression test
Depending on test engineering and project management, the philosophy could
be: (1) to rerun everything or (2) rerun only those test cases affected
by a changed. In either case everything should be tracked using the defect
tracking or reporting form. An example set of form is included at the end
of this lesson.
The master test plan is the document that identifies a general plan for when, how or what level of regression test is applicable. The master test plan guidelines must be taken into account if this is what the client approved. The project standards will have guidelines on an acceptable level of regression test. For two examples look at DoD-STD-2167A and DoD-STD-498 of which many samples can be found using an internet search.
The test manager must Schedule the regression test to accommodate QA and test engineering. The level of regression test may need to be adjusted to accommodate a reduced schedule or shift availability of personnel.
When deciding which test cases to rerun the test engineer must consider the severity, category, and number of errors that were fixed and will be tested. Sometimes not all test cases will be executed during regression test.
Regression test activitiesThe regression test activities are the same as all other test phases. They are:
- Test Execution
- Logging problems detected
- Retest resolved problems
- Obtain witness signatures
If the test engineer is using a capture or test replay tool for testing and the test cases need to be witnessed by the client, QA, or security, the test engineer will need to decide ahead of time how the witnesses are going to verify each step and the expected results from the automated output report. The example test procedure data sheet or form is necessary. An example of this form is at the end of this lesson.
When does test engineering begin regression test? The test engineer must schedule the hardware and software resources and the personnel needed to begin each test activity. If the software is well divided, such as with CSCIs, the test engineer can begin anytime after each CSCI has completed function testing. Otherwise, test engineering will probably want to wait until all function test cases have been executed.
The entry criteria and input activities for Function Test are:
- Successful completion of unit and integration test.
- Completion of at least one dry run.
- Completion of a Test Readiness Review (TRR). Test engineering must successfully exit the TRR and have test-related action items closed.
- Intact & operational hardware & software test environment. Function Test is generally conducted at the development site. The issue regarding the test environment is whether a hardware and software test environment is dedicated to test or must be shared with the development activities. If this is the case, test engineering needs to plan for verifying the system mimics the operational environment and does not have development tools still in the package. If this is the case, it should be documented as a risk. Sharing may also impact: schedule, time to resolve problems, cleaning the system, etc.
- Installed software configuration management load build. Testing must be conducted from the configuration controlled code. The build should be built from CM controlled libraries and authorized by CM.
- Completion and attainment of necessary tools & drivers. Any necessary tools should be installed and verified as operational before beginning the function test activities.
The exit criteria & outputs for function test are:
- 100% of the test cases have been exposed. Exposed, means that a test case has been executed during the current test phase and the test case is procedurally error free.
- 100% of test cases are successful or there is a written agreement with the client for acceptance. Procedures for handling unsuccessful test cases should be documented in the master test plan.
- All problems are resolved or a written agreement with the client indicating acceptance. Procedures for handling unresolved or non-reproducible problem should be documented in the master test plan.
- Change requests resulting from the function test must be written. Any change requests, such as engineering change proposals or requests for waivers must be filled out.
- The test report is completed and delivered to the client. This is usually done the between 30 to 45 days following test execution. During this period test engineering must also begin system test.
System test is typically performed as part of formal qualification test (FQT) for Government contracts. System test can be consider just another separate test phase for commercial contracts. Function test concentrates on the system requirements.
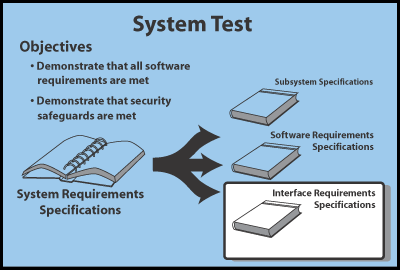
The System Test graphic illustrates that the system requirements specification
is analyzed and the software requirements are mapped into software and
interface specifications. However, some of the system requirements do
not get mapped into software requirements. It is these requirements that
are tested in the system test phase. For large contracts, there may be
multiple documents specifying the system level requirements.
Test engineering may want to isolate performance, stress, and other system oriented requirements in their own grouping, regardless of whether the requirements are mapped to the software level. Test engineering will need to perform end-to-end testing during system test. System test for security is only relevant to systems with security related requirements.
These are a few examples of test techniques are applicable to system test. The test techniques are:
- Volume and stress
- Performance
- Reliability, maintainability, and availability
- Degradation and recovery
- Configuration
- Installation
- Environmental
- System User help and information
System Test Tools to consider.
- Network performance measuring tools are beneficial in measuring loading, stress, and performance issues. These tools are used to set up user scenarios and then model the number of users. Rational Test Factory tool is an example of a test case capture replay tool with automated scripting capabilities. Automated test scripts can be used to evaluate the network performance.
- Memory leakage tools are useful when conducting stress tests by repeated and intense operations in a period of time. They are especially beneficial if these stress tests are automated.
- The other tools used in functional testing apply here also.
The system test activities and regression testing scope are the same as for function test.
The entry criteria and input activities for system test are:
- Successful completion of function regression test
- Intact & operational hardware & software test environment
- Installed formal configuration build
- Completion and attainment of necessary test tools and drivers
The exit criteria and outputs for system test are:
- 100% of the test cases have been exposed
- 100% of test cases are successful or there is a written agreement with the client for acceptance
- All problems are resolved or a written agreement with the client indicating acceptance
- Change requests resulting from the system test must be written
- The test report is completed and delivered to the client