Experimenting
with X.509 Digital Certificates
· Required setup:
a.
Pre-requisites: Before running this script, in
your pipenv shell, run 'pipenv install pyOpenSSL'.
b. In the script, import OpenSSL.crypto: from OpenSSL import crypto
·
API References:
a. pyOpenSSL crypto: https://www.pyopenssl.org/en/latest/api/crypto.html
b.
X509
reference: https://cryptography.io/en/latest/x509/reference/
#from cryptography import X509
NOTE: Use to_cryptography( ) to convert an OpenSSL
certificate to an X509 certificate when, for example, you want to use a method
or attribute defined in the X509 library. See example codes below.
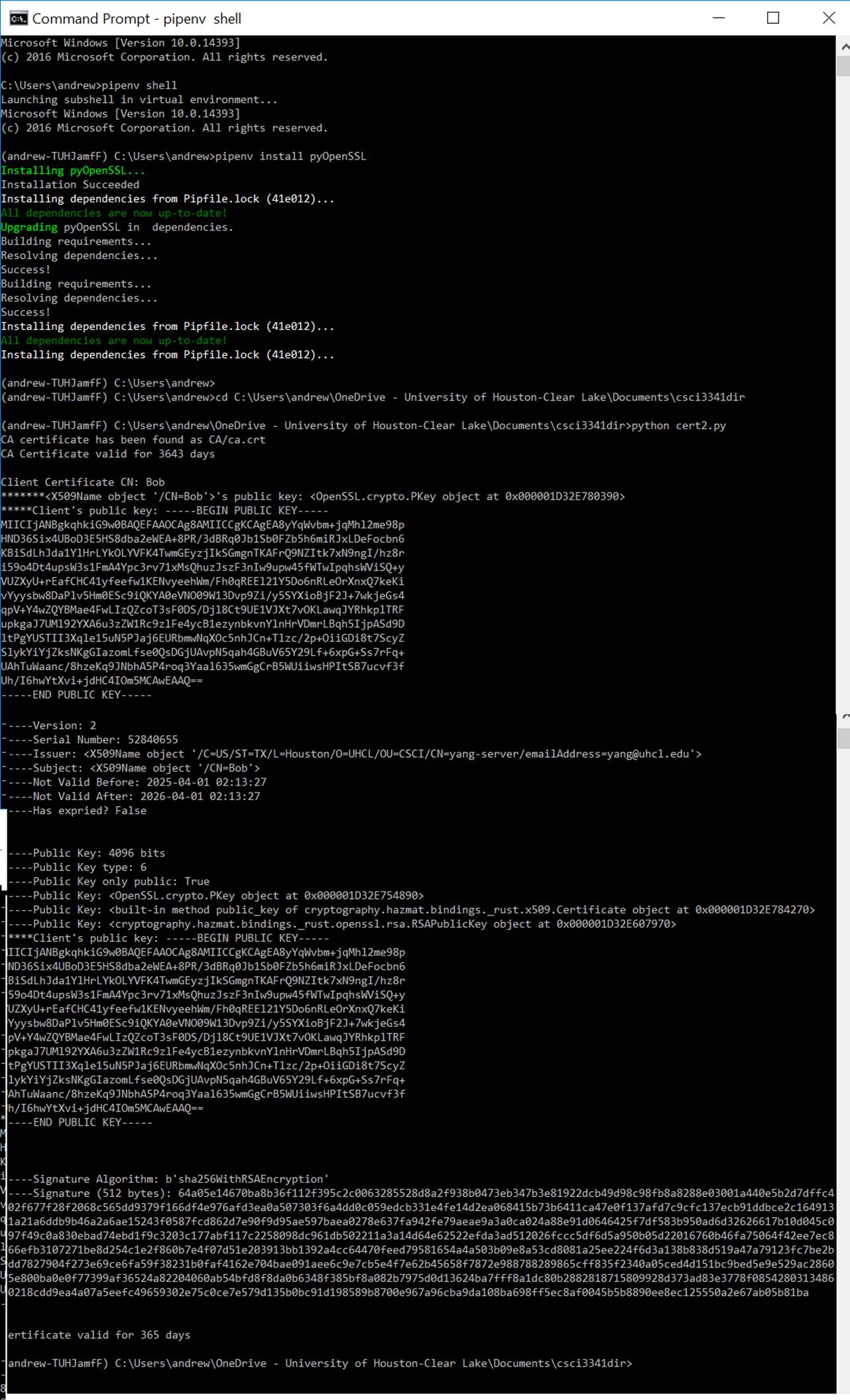
In the sample program shown in Figure 1, a self-signed CA certificate is first created.
The CA certificate is then used to sign a client’s certificate.
|
#!/usr/bin/env python3 # # Description :- Generate self-signed
CA and certificates. # Author :- Muhammed
Iqbal <iquzart@hotmail.com> # original github link: https://github.com/iquzart/python-digital-certificate # Pre-requisites: Before
running this script, in your pipenv shell, run 'pipenv install pyOpenSSL'. # # Revised by : T. Andrew
Yang # Date : March
25, 2025 # import random import os from datetime import datetime # pyOpenSSL crypto: https://www.pyopenssl.org/en/latest/api/crypto.html from OpenSSL import crypto def create_CA (root_ca_path,
key_path): ''' Create CA and Key''' ca_key = crypto.PKey()
#private key: https://www.pyopenssl.org/en/latest/api/crypto.html
ca_key.generate_key(crypto.TYPE_RSA, 4096) ca_cert = crypto.X509() ca_cert.set_version(2)
#Version.v3: 2
#https://cryptography.io/en/latest/x509/reference/#x-509-certificate-object
ca_cert.set_serial_number(random.randint(50000000, 100000000)) ca_subj =
ca_cert.get_subject() ca_subj.countryName = input("Country
Name (2 letter code) [XX]: ") ca_subj.stateOrProvinceName
= input("State or Province Name (full name) []: ") ca_subj.localityName =
input("Locality Name (eg, city) [Default City]: ") ca_subj.organizationName
= input("Organization Name (eg, company) [Default Company Ltd]: ") ca_subj.organizationalUnitName
= input("Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []: ") ca_subj.commonName
= input("Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) []:
") ca_subj.emailAddress
= input("Email Address []: ") ca_cert.set_issuer(ca_subj) ca_cert.set_pubkey(ca_key) ca_cert.add_extensions([ crypto.X509Extension(b"subjectKeyIdentifier", False, b"hash", subject=ca_cert), ]) ca_cert.add_extensions([ crypto.X509Extension(b"authorityKeyIdentifier", False, b"keyid:always,issuer", issuer=ca_cert), ]) ca_cert.add_extensions([ crypto.X509Extension(b"basicConstraints", True, b"CA:TRUE"), #crypto.X509Extension(b"keyUsage", True, b"digitalSignature,
keyCertSign, cRLSign"), ]) ca_cert.gmtime_adj_notBefore(0) ca_cert.gmtime_adj_notAfter(10*365*24*60*60) ca_cert.sign(ca_key,
'sha256') #ca_key is the CA's private key; the CA's cert is self-signed # Save certificate with open(root_ca_path,
"wt") as f: f.write(crypto.dump_certificate(crypto.FILETYPE_PEM,
ca_cert).decode("utf-8")) # Save private key with open(key_path, "wt") as f: f.write(crypto.dump_privatekey(crypto.FILETYPE_PEM,
ca_key).decode("utf-8")) def load_CA (root_ca_path, key_path): ''' Load CA and Key''' with open(root_ca_path,
"r") as f: ca_cert = crypto.load_certificate(crypto.FILETYPE_PEM,
f.read()) with open(key_path,
"r") as f: ca_key = crypto.load_privatekey(crypto.FILETYPE_PEM,
f.read()) return ca_cert, ca_key def CA_verification (ca_cert): ''' Varify
the CA certificate ''' ca_expiry
= datetime.strptime(str(ca_cert.get_notAfter(), 'utf-8'),"%Y%m%d%H%M%SZ") now = datetime.now() validity = (ca_expiry - now).days print ("CA Certificate
valid for {} days".format(validity)) def create_cert (ca_cert, ca_subj, ca_key, client_cn): ''' Create Client
certificate ''' client_key
= crypto.PKey() client_key.generate_key(crypto.TYPE_RSA,
4096) client_cert
= crypto.X509() client_cert.set_version(2) client_cert.set_serial_number(random.randint(50000000,
100000000)) client_subj
= client_cert.get_subject() client_subj.commonName
= client_cn client_cert.set_issuer(ca_subj) client_cert.set_pubkey(client_key) print(f"*******{client_cert.get_subject()}'s public key: {client_cert.get_pubkey()}") client_cert.gmtime_adj_notBefore(0) client_cert.gmtime_adj_notAfter(365*24*60*60) client_cert.sign(ca_key,
'sha256') #Use the CA's private key to sign the client's cert with open(client_cn + ".crt",
"wt") as f: f.write(crypto.dump_certificate(crypto.FILETYPE_PEM,
client_cert).decode("utf-8")) with open(client_cn + ".key", "wt")
as f: f.write(crypto.dump_privatekey(crypto.FILETYPE_PEM,
client_key).decode("utf-8")) public_key = crypto.dump_publickey(crypto.FILETYPE_PEM,
client_key).decode("utf-8") print(f"*****Client's
public key: {public_key}") return client_cert def client_verification (ca_cert, ca_key, client_cert): print("\n") # First, check whether the
certificate has expired or not cert_expiry
= datetime.strptime(str(client_cert.get_notAfter(), 'utf-8'),"%Y%m%d%H%M%SZ") now = datetime.now() validity = (cert_expiry - now).days print ("Certificate
valid for {} days".format(validity)) # Q: How would you verify the signature in a
client's certificate? # Ans: Use the
CA's public key to verify a client's certificate. def print_cert (cert): print(f"-----Version:
{cert.get_version()}") print(f"-----Serial
Number: {cert.get_serial_number()}") print(f"-----Issuer: {cert.get_issuer()}") print(f"-----Subject:
{cert.get_subject()}") notBefore
= datetime.strptime(str(cert.get_notBefore(), 'utf-8'),"%Y%m%d%H%M%SZ") print(f"-----Not Valid
Before: {notBefore}") notAfter
= datetime.strptime(str(cert.get_notAfter(), 'utf-8'),"%Y%m%d%H%M%SZ") print(f"-----Not Valid
After: {notAfter}") print(f"-----Has expried? {cert.has_expired()}") print("\n") print(f"-----Public
Key: {cert.get_pubkey().bits()} bits") print(f"-----Public
Key type: {cert.get_pubkey().type()}") print(f"-----Public
Key only public: {cert.get_pubkey()._only_public}") print(f"-----Public
Key: {cert.get_pubkey()}") cryptCert
= cert.to_cryptography() print(f"-----Public
Key: {cryptCert.public_key}") print(f"-----Public
Key: {cryptCert.public_key()}") # Export the key to bytes # Attempt 1: not working #public_key = cryptCert.public_key #pubKeyString
= crypto.dump_publickey(crypto.FILETYPE_PEM,public_key)
#https://www.pyopenssl.org/en/latest/api/crypto.html #print(f"Public
Key: {pubKeyString}") # Attempt 2 public_key = cert.get_pubkey() public_key_bytes
= crypto.dump_publickey(crypto.FILETYPE_PEM,
public_key).decode("utf-8") print(f"*****Client's
public key: {public_key_bytes}") print("\n") print(f"-----Signature
Algorithm: {cert.get_signature_algorithm()}")
#print(f"-----Signature: {cert.signature}") #somehow this does not work cryptCert
= cert.to_cryptography() #workaround to get the
signature size = len(cryptCert.signature) print(f"-----Signature
({size} bytes): {cryptCert.signature.hex()}") def main(): '''Create self signed certificates''' #First, creaate the CA certificate: key_path = "CA/ca.key" root_ca_path =
"CA/ca.crt" if not os.path.exists('CA'): print ("Creating
CA driectory") os.makedirs('CA') if not os.path.exists(root_ca_path): print ("Creating
CA Certificate, Please provide the values") create_CA(root_ca_path,
key_path) print ("Created CA
Certificate") ca_cert, ca_key = load_CA(root_ca_path, key_path) CA_verification(ca_cert) else: print ("CA certificate has been
found as {}".format(root_ca_path)) ca_cert, ca_key = load_CA(root_ca_path, key_path) CA_verification(ca_cert) #Then, create a client's
certificate signed by the CA while True: client_cn
= input("\nClient Certificate CN: ") if client_cn
!= '': break else: print ("Please
provide a valid CN for client certificate") ca_subject
= ca_cert.get_subject() client_cert
= create_cert(ca_cert, ca_subject,
ca_key, client_cn) print_cert(client_cert) client_verification(ca_cert,
ca_key, client_cert) if __name__ == "__main__": main() |
Figure 1: The source program
(cert2.py)
|
|
Figure 2: Screen output when
running the source program