Topic: Keyed Hashing and Data Authentication
††††††††††† Figure 1: A sample script using hmac
Figure
2: Alice verifies Bobís identity with a shared key and an HMAC function
††††††††††† Figure 3: A Python script that simulates the above scenario
Figure 1: A sample
script using hmac
|
import hashlib import hmac # reference: https://docs.python.org/3/library/hmac.html msg1 = 'message' print("\nhmac using sha256 ...........") hmac_sha256 = hmac.new(key=b'key1', msg=msg1.encode(), digestmod=hashlib.sha256) #A string must be encoded first before hashing. print("original mesg: ", msg1) print("mac produced by digest(): ", hmac_sha256.digest()) print("mac produced by hexdigest(): ", hmac_sha256.hexdigest()) print("size: ", hmac_sha256.digest_size) print("\nhmac using md5 ...........") hmac_md5 = hmac.new(key=b'key1', msg=msg1.encode(), digestmod=hashlib.md5) print("original mesg: ", msg1) print("mac produced by digest(): ", hmac_md5.digest()) print("mac produced by hexdigest(): ", hmac_md5.hexdigest()) print("size: ", hmac_md5.digest_size) digest1 = hmac_md5.hexdigest() #change the message to msg2 msg2 = "message2" hmac_sha256.update(msg2.encode()) print("\nhmac using sha256 ...........") print("new mesg: ", msg2) print("mac produced by hexdigest(): ", hmac_sha256.hexdigest()) print("size: ", hmac_sha256.digest_size) hmac_md5.update(msg2.encode()) print("\nhmac using md5 ...........") print("new mesg: ", msg2) print("mac produced by hexdigest(): ", hmac_md5.hexdigest()) print("size: ", hmac_md5.digest_size) digest2 = hmac_md5.hexdigest() digest2b = hmac_md5.hexdigest() #DO NOT compare two hashes using ==; it is subject to timing attack. #Use compare_digest() instead if ( hmac.compare_digest(digest1, digest2)): †† †print(digest1, "is equal to ", digest2) else: ††† print(digest1, "is NOT equal to ", digest2) if ( hmac.compare_digest(digest2, digest2b)): ††† print(digest2, "is equal to ", digest2b) else: ††† print(digest2, "is NOT equal to ", digest2b) |
Data
Authentication using HMAC:
Figure 2: Alice verifies Bobís identity with a
shared key and an HMAC function (Figure 3.3 of the textbook)
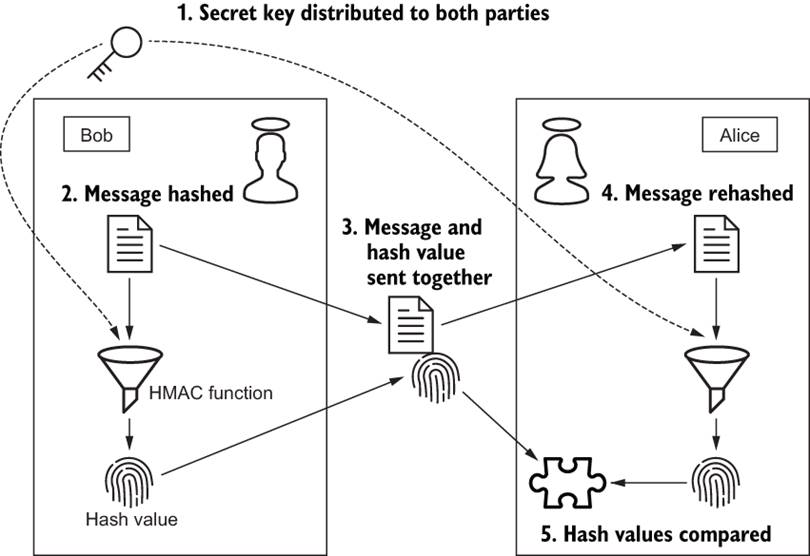
Figure 3: A Python
script that simulates the above scenario
|
#This script simulates that Bob, the sender, sends a message and #† the
message's hash to Alice, the receiver. #† Alice reads both the message
and the accompanied hash and then #† verifies the integrity of
the received message using hmac by comparing #† the
accompanied hash with a freshly generated hash. import hashlib import hmac import json def Bob(): †† hmac_sha256 = hmac.new(b'shared_key', digestmod=hashlib.sha256) †† message = b'from Bob to Alice' †† hmac_sha256.update(message) †† hash_value
= hmac_sha256.hexdigest() † †† authenticated_msg
= { ††††† 'message': list(message), ††††† 'hash_value':
hash_value, } †† print("message: ",
authenticated_msg['message']) †† print("hash: ", authenticated_msg['hash_value']) †† print("authenticated_msg: ", authenticated_msg) ††††††††††††† †† outbound_msg_to_alice
= json.dumps(authenticated_msg) †† print("outbound_msg_to_alice: ", outbound_msg_to_alice) †† return outbound_msg_to_alice †† def Alice (inbound_msg_from_bob): †† authenticated_msg
= json.loads(inbound_msg_from_bob) †† message = bytes(authenticated_msg['message']) †† received_hash
= authenticated_msg['hash_value'] †† print("\nTrying to verify the message: ", message, †††††† "and hash: ", received_hash) †† hmac_sha256 = hmac.new(b'shared_key', digestmod=hashlib.sha256) †† hmac_sha256.update(message) †† hash_value
= hmac_sha256.hexdigest() † †† #if hash_value
== authenticated_msg['hash_value']: †† if hmac.compare_digest(hash_value, received_hash): ††††††††††††† †† print('trust message') †† else: ††††††††††††† †† print('cannot trust message') message = Bob() Alice(message) |
Figure 4: Examples of
using json.dumps( ) and json.loads()
|
# Examples of using json.dumps() and json.loads()
in Python # source: Google Search Labs|AI Overview (keywords: example python json dumps loads) † import json # Example data (Python dictionary) data = { †††
"name": "John Doe", †††
"age": 30, †††
"city": "New York", †††
"is_student": False, †††
"courses": ["Math", "Science"] } # Using json.dumps()
to convert Python dictionary to JSON string json_string = json.dumps(data, indent=4) # indent for
pretty printing print("JSON string:") print(json_string) # Using json.loads()
to convert JSON string back to Python dictionary parsed_data = json.loads(json_string) print("\nParsed
Python dictionary:") print(parsed_data) # Accessing data from the parsed
dictionary print("\nName:",
parsed_data["name"]) print("Age:", parsed_data["age"]) print("Is student:", parsed_data["is_student"]) print("First course:", parsed_data["courses"][0]) |