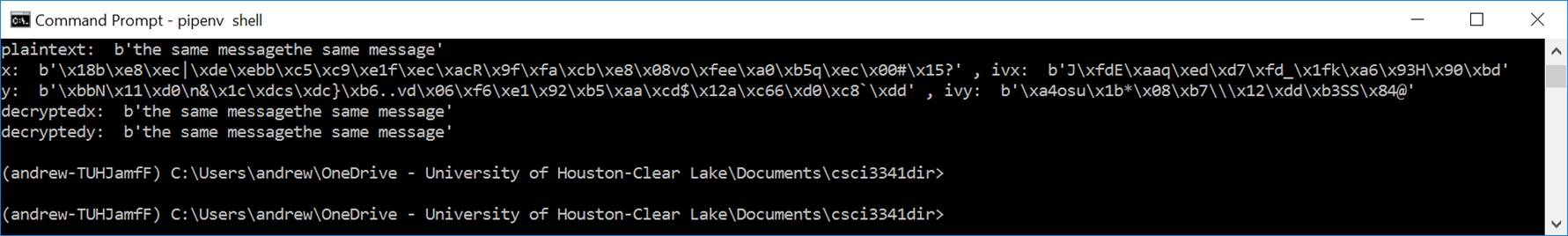
A. Set up pipenv on your system.
- Pipenv: Python Dev Workflow for Humans: https://pipenv.pypa.io/en/latest/
- Pipenv Installation: https://pipenv.pypa.io/en/latest/installation.html
NOTE: Make sure the PATH environment variable is configured correctly.
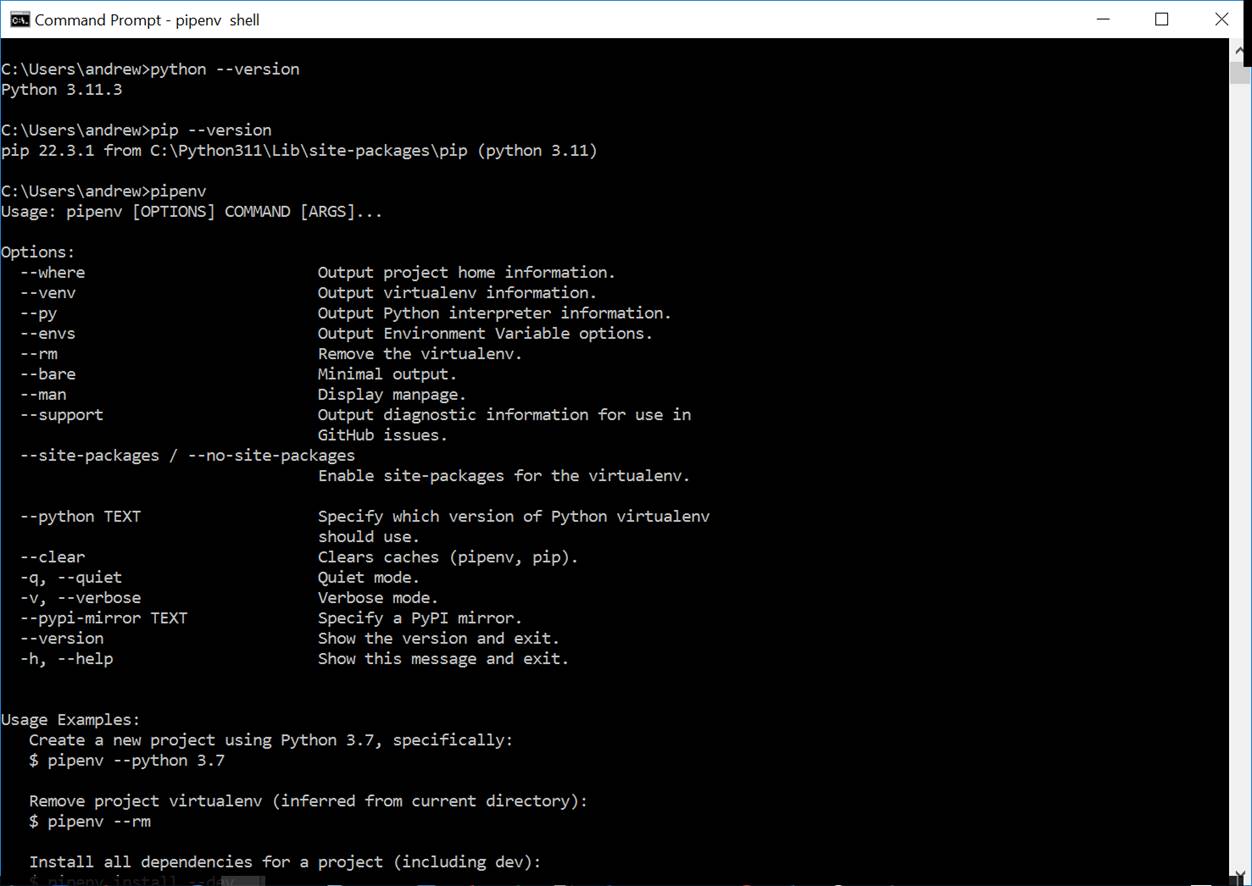
B. Set up a virtualenv for your project.
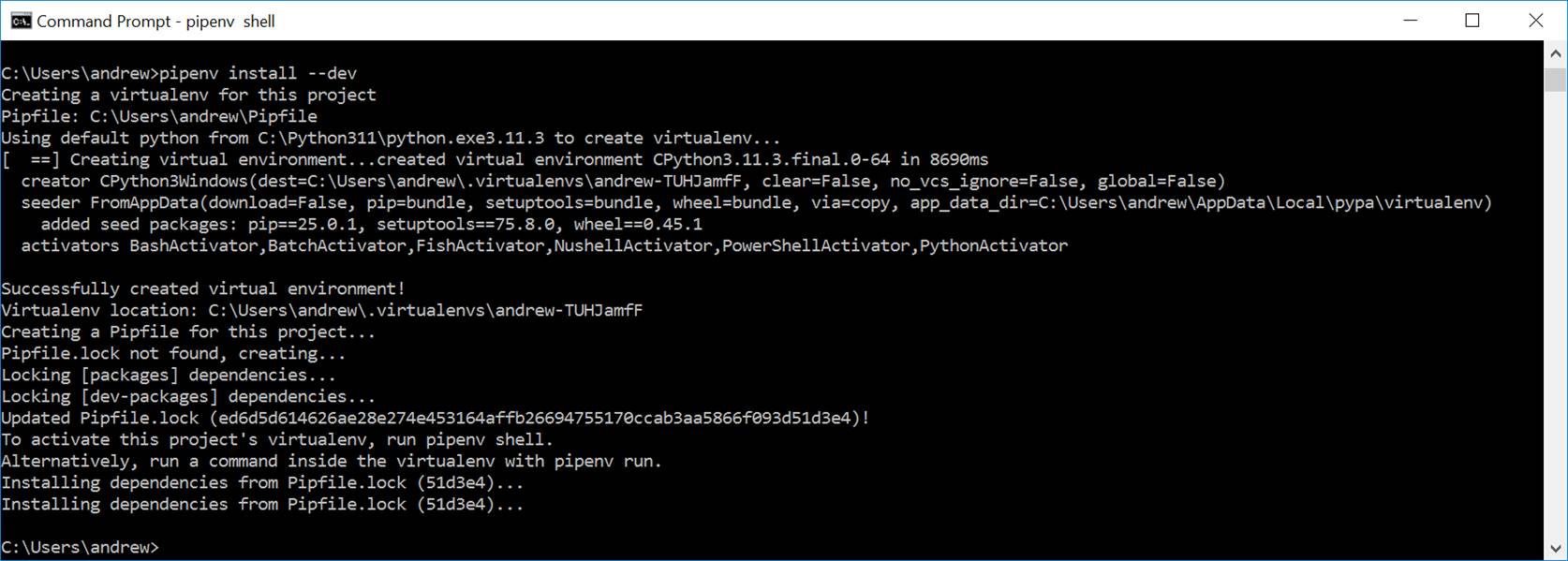
C. Create a virtual shell and install the cryptography package.
D. Run the following sample script to encrypt something using AES in CBC (Cipher Block Chaining) mode.
|
import secrets from cryptography.hazmat.backends import default_backend from cryptography.hazmat.primitives.ciphers
import (Cipher, algorithms, modes) key = b'key must be 128, 196 or 256 bits' def encrypt(data): iv
= secrets.token_bytes(16) # generates a random byte
string. cipher = Cipher( algorithms.AES(key), modes.CBC(iv), backend=default_backend()) encryptor
= cipher.encryptor() return encryptor.update(data)
+ encryptor.finalize() plaintext = b'the same message' * 2 print("plaintext: ", plaintext) x = encrypt(plaintext) print("x: ", x) y = encrypt(plaintext) print("y: ", y) # CBC mode
produces different ciphertexts # when encrypting identical plaintexts with the same key. # CBC mode
achieves this by individualizing plaintext with # an initialization vector (IV). print("Is x[:16] == x[16:]?", x[:16] == x[16:]) print("Is x == y?", x == y) # Q: How to decrypt x and y? |
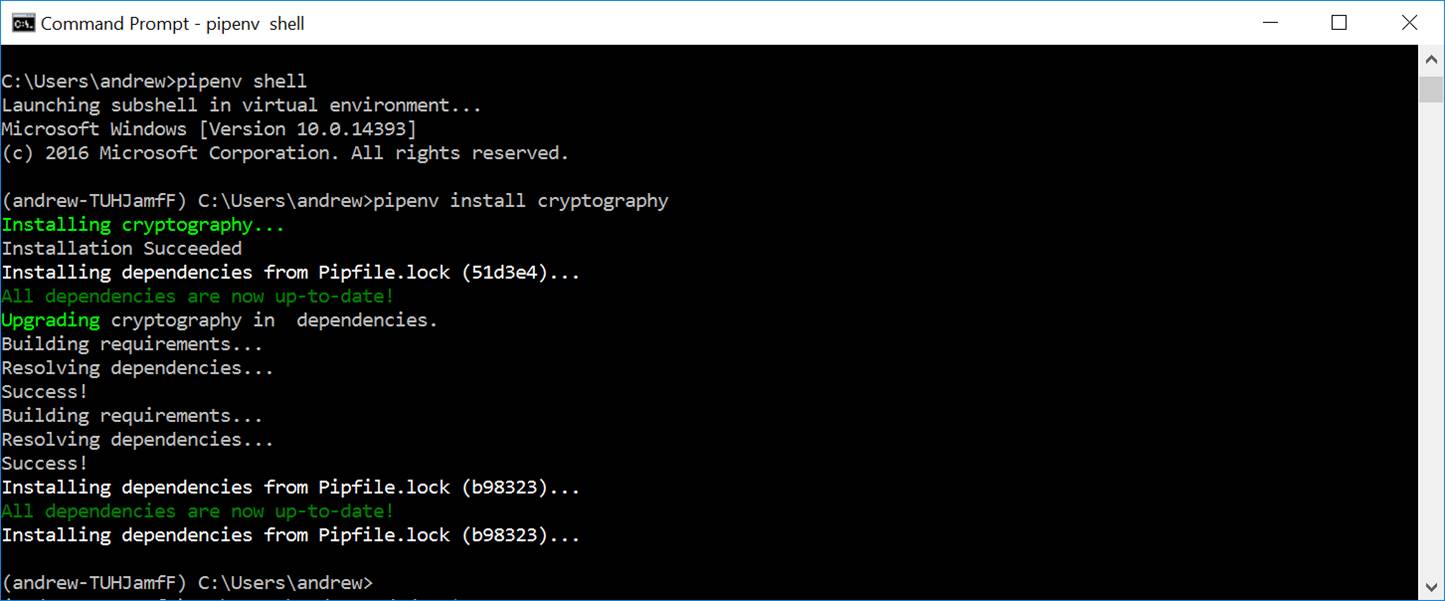
Q: How would you revise the above script to decrypt x and y successfully?
Hint: The decryption process needs not only the ciphertext and the key, but also the iv used during the encryption process.
|
import secrets from cryptography.hazmat.backends import default_backend from cryptography.hazmat.primitives.ciphers
import ( Cipher, algorithms, modes) key = b'key must be 128, 196 or 256 bits' def encrypt(data): iv
= secrets.token_bytes(16) # generates a random byte
string. cipher = Cipher( algorithms.AES(key), modes.CBC(iv), backend=default_backend()) encryptor
= cipher.encryptor() return encryptor.update(data)
+ encryptor.finalize(), iv plaintext = b'the same message' * 2 print("plaintext: ", plaintext) x, ivx = encrypt(plaintext) print("x: ", x, ", ivx:
", ivx) y, ivy = encrypt(plaintext) print("y: ", y, ", ivy: ", ivy) # CBC mode produces different ciphertexts # when encrypting identical plaintexts with
the same key. # CBC mode achieves this by individualizing plaintext with # an initialization vector (IV). #print("Is x[:16] == x[16:]?", x[:16] == x[16:]) #print("Is x == y?", x == y) # Q1: How to decrypt x and y? cipherx = Cipher( algorithms.AES(key), modes.CBC(ivx), backend=default_backend()) decryptor = cipherx.decryptor() decryptedx = decryptor.update(x)
+ decryptor.finalize() print("decryptedx: ", decryptedx) ciphery = Cipher( algorithms.AES(key), modes.CBC(ivy), backend=default_backend()) decryptor = ciphery.decryptor() decryptedy = decryptor.update(y)
+ decryptor.finalize() print("decryptedy: ", decryptedy) # Q2: How to reduce the redundancy in coding? |