|
T. Andrew Yang
|
Last updated: 7/19/2022: correction of Lab 2.d 6/6/2022: first posted |
||||||
NOTE: When preparing your
answers, you are welcome to use any resources, including the text books.
However, make sure you properly cite the work of other researchers or
professionals. Visit http://cse.uhcl.edu/yang/citing.htm for more information about cited references. Warning: Missing or improper cited references in your
answers will result in poor scores.
Total: 100 points
1.
(5 pts)
Visit the class discussion group in the Blackboard. Post a message with your
full name as the subject line. In your post, briefly introduce yourself,
including your full name, your major, and one or two items that you most desire
to learn in this class. Throughout this class, you shall regularly participate
at the discussion group to find recent announcements, reminders, and
discussions.
2.
Cyber
attacks: Explain what each of the following attacks is. Cite
your source(s). Note: Not all information
published on the web are correct. Discern the validity of the information
you use by, for example, comparing them with what you have learned from the
textbooks and the class discussions.
a.
(10 pts) Replay attacks
b.
(10 pts) Man-in-the-middle
attacks
c. (10 pts) Explain the relationship
between replay attacks and Denial of Service (DoS) attacks. Hint:
How would the hacker use replay attacks to
cause Denial of Service?
d. (10 pts) Explain the differences between replay attacks and man-in-the-middle attacks.
3.
In an
online banking application, the customer may transfer fund between the saving account
and the checking account.
a.
(5 pts) Explain
what data integrity means in this context.
b.
(5 pts) Explain
what origin integrity means in this context.
c.
(5 pts) Explain
what availability means in this context.
d.
(5 pts) Explain
what confidentiality means in this context.
e.
(5 pts) Explain
what non-repudiability means in this context.
4.
Hands-on
lab
a. To prepare your computer for the remaining hands-on labs, set up your
computer according to instructions given at this page: https://seedsecuritylabs.org/lab_env.html
a.1. Download
and install the virtual box first.
a.2. Next,
download the SEED Ubuntu16.04 VM image
file to a folder in your computer.
a.3. Unzip and
copy the VM images to a folder.
a.4. Configure the virtual box and create a new virtual machine with the same
name as your full name (e.g., JohnDoe as the name of
the VM).
a.5. To hand in:
a.5.1.
(10
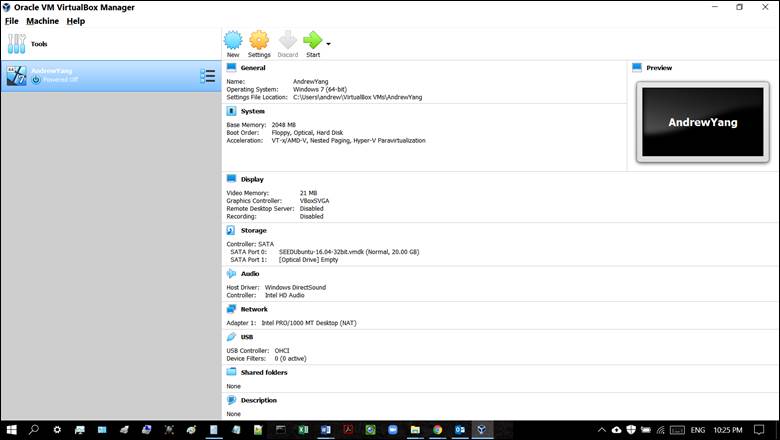
pts) Print a screenshot of your VM created above (in
6.1.4). Note: Name the VM using your full name. Figure 2-1 shows a sample
screenshot.
|
|
Figure 2-1:
Sample screenshot of a VM
|
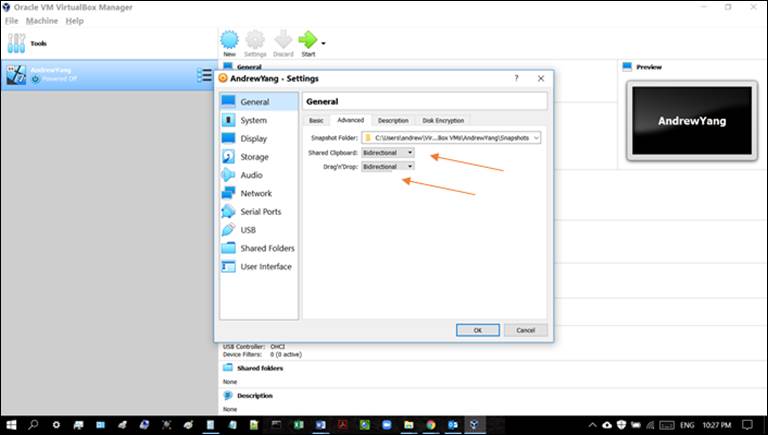
Note: As shown in
Figure 2-2, in order to enable shared clipboard between the VM and your
computer’s OS, be sure to configure, in Settings/General/Advanced, both ‘Shared
Clipboard’ and ‘Drag’n’Drop’ to bidirectional.
|
|
Figure 2-2:
VM settings to enable shared clipboard
|
a.5.2.
Answer the following questions:
a.5.2.1.
(5
pts) What is a virtual box? Hint: Explain its
relationship to the operating system. What is the role played by the virtual
box?
a.5.2.2.
(5
pts) What is the role played by the SEED Ubuntu16.04 VM image?
a.5.2.3.
(5
pts) How many VMs can you run simultaneously within a
virtual box?
a.5.2.4.
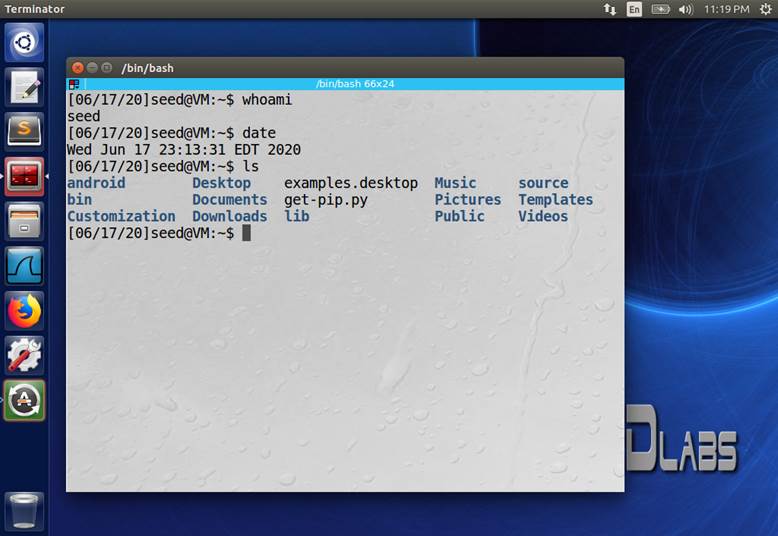
(5
pts) Start the VM created above in 6.1. Click the Terminator icon to activate a terminal
window within the VM. Enter the following three commands into the terminal
window: whoami, date, ls. Take a screenshot of the terminal window. See Figure 2-3 for an example
screenshot.
|
|
Figure 2-3:
Sample screenshot of a terminal window in the virtual box
|
Go to
the Index
Total:
100 points
1.
(10 pts) Review how the Euclid Algorithm works by entering 120 and 77 as
the two input numbers using the online gcd calculator at https://www.calculatorsoup.com/calculators/math/gcf-euclids-algorithm.php.
Use the Extended Euclidian Algorithm (EEA) to find the values of x
and y for the equation 120x + 77y = 1. Show the intermediate steps.
NOTE: Always verify the derived values to ensure that they’d satisfy the given
equation. When necessary, switch the values of x and y.
2.
RSA key-pair generator
a.
(5 pts) Given two prime numbers, p = 13 and q = 23. The first step of
generating an RSA key-pair is to calculate the values of n and totient(n). Show
how the two values are calculated.
b.
(5 pts) Given n and totient(n), the public key (e) is selected, by making
sure e < n and gcd(e, totient(n)) = 1. Can the
number 77 be selected as the public key of this key pair? Justify your
answer.
c.
(10 pts) Show the first 30 (or all of the) numbers in the set of potential
public keys that may be chosen, considering the values of n and totient(n)
derived above.
d.
(10 pts) Let the public key e be 51 53.
Solve e*d mod totient(n) = 1 to determine the private key d. Show the
detailed steps. Hint: Use EEA. NOTE: Always verify the derived private key
by checking whether it’d satisfy the original equation.
3.
(10 pts) Digital Signature Algorithms: Are there any drawbacks with the Digital Signature? Under what
circumstances it may not be effective to implement Digital Signatures?
4.
Hands-on
lab
NOTE: Configure and run your hands-on labs in the virtual box that you set up
earlier in the previous lab.
4.1. Study the Description of the “Crypto Lab -- Secret-Key Encryption” (https://seedsecuritylabs.org/Labs_16.04/PDF/Crypto_Encryption.pdf), in particular Task 2: Encryption using Different Ciphers and Modes.
4.2. Use the first question of this lab as the content of the initial plain.txt file.
4.3. Encrypt the plain.txt file into cipher.bin file using the AES-128-CBC
cipher. Save the content of the ciphertext. (Case #1 in Table 4.1)
4.4. Modify the plain.txt file by adding a sentence like ‘My name is …’ at the
beginning of the file. NOTE:
Use your own full name. Encrypt the modified file to produce
a new cipher file. Save the content of the ciphertext. (Case #2 in Table 4.1)
4.5. Modify the plain.txt file by making the first sentence as a standalone
line by itself. Encrypt the modified file to produce a new cipher file. Save
the content of the ciphertext. (Case #3 in Table 4.1)
4.6. (40 pts) Table 4.1
shows the three cases described above and the respective plaintext and
ciphertext. Generate a table like this from your own files.
Table 4.1: Three cases of comparison between the
plaintext and the ciphertext using AES-128-CBC
encryption
|
Cases |
Content of
plaintext files |
Content of
the ciphertext files (in hex) |
|
#1 |
Review how the Euclid
Algorithm works by entering 100 and 77 as the two input numbers using the
online gcd calculator at https://www.calculatorsoup.com/calculators/math/gcf-euclids-algorithm.php. |
B4 21 13 1A EC 60 02 42 C7
A3 36 FD 2E 1C 42 D8 3B F6 C8 DD 95 17 DB 37 1F 2E 68 C1 CD 23 33 61 83 FD 0B
FC F5 FC 6E F7 E1 D7 62 18 E3 2F 6D 18 68 81 28 14 0C C2 F3 56 F9 64 03 2E 05
26 B6 BE 4F 65 53 F1 D9 71 1B 38 03 FB BA CD BA E7 B9 4E 9D 97 53 29 F8 05 6F
0A 7E 7C 8A 5A 73 6C B2 FB E5 D6 EB F0 18 D7 C0 E7 9C 7A A0 44 7B DE 89 8E 25
95 12 CD 49 69 D0 50 F4 45 17 03 3B C6 ED 43 6D 3E DB 4A C9 D2 B6 48 DF BA F1
95 D0 E1 65 2E 60 E0 6E C5 02 2F 09 8E E7 9B 63 FC 25 46 1B 0A 53 0A 7A 60 E1
C6 B1 11 B4 FF 88 B0 0A 51 08 27 70 B4 AE 00 4D 82 B9 23 CC 25 D4 D2 95 AC 55
52 72 D9 53 B8 47 36 B6 17 4E FC E5 B4 E5 CE 38 F9 |
|
#2 |
My name is John Doe. Review how
the Euclid Algorithm works by entering 100 and 77 as the two input numbers
using the online gcd calculator at
https://www.calculatorsoup.com/calculators/math/gcf-euclids-algorithm.php. |
9C D9 B8 FF A7 6A 89 47 E1 68 90 F5 DE 4C 1D A7 90 9D BE CD BF 41 6B FC 97 8C 7D D6 4A F6 27 04 FC A8
2D 3D F3 84 E4 24 CC 52 C8 F5 02 FE CB A1 46 C5 FB 00 4C D3 5D 28 C4 C7 7B AE
0F 03 B1 15 0D AD B1 CE 58 7B CE FB E7 4D 6A B5 76 3A 97 E4 33 A9 2E 78 B2 40
AE 88 9B 61 F2 AF 98 4C A1 03 3E 25 9B 2E B9 C3 51 A1 F6 22 E2 F8 C5 14 1A 4B
8B BB DC FD A1 AF D1 1E 54 1E 39 FF 13 D5 6B F8 D5 60 CE 93 BE D4 46 17 BC 1B
3D F3 B8 7E 4B E7 38 81 33 12 59 16 EC CF BB C0 5C 0E A5 74 28 D0 26 9F 84 7A
A6 4A BC B1 64 E2 56 48 3F 2C 8D 93 1D 48 C4 B4 5A 12 C6 16 75 F0 E8 93 FC 1B
38 8D CA 62 7D 67 04 A9 A4 FD B8 AE F0 FD 39 FA 30 94 FB 69 FD 61 88 68 BE 24
E8 3E CF D4 D9 43 BD 4F |
|
#3 |
My name is John Doe. Review how the Euclid
Algorithm works by entering 100 and 77 as the two input numbers using the
online gcd calculator at https://www.calculatorsoup.com/calculators/math/gcf-euclids-algorithm.php. |
9C D9 B8 FF A7 6A 89 47 E1 68 90 F5 DE 4C 1D A7 B4 51 37 39 16 BB C9 D3 A3 85 74 44 6E 70 50 0B 07
0C 2B E1 79 84 17 D9 32 90 5D E6 E4 F7 BE F9 18 B0 E9 63 8B 00 60 27 DE E2 8C
E5 30 4D B7 08 47 B7 13 10 9D FD E3 08 4B DC B5 3C FD D0 A3 F6 CA 6E 6F 94 BE
64 27 51 6C 8E 08 F2 11 F5 74 53 3D 9E 18 F7 98 E2 05 04 88 E8 AE 84 53 FE B7
A0 5B E4 7D 87 DD B6 8D 75 9D C0 E2 0D D9 33 4D A2 CE 89 E5 8F 4D A9 98 C8 A2
F4 D5 41 FF 90 61 EA E6 74 7A 7C 2E 04 A3 BE 20 1A C3 33 97 B1 89 36 F9 CC 4B
C6 D6 3B 0B E2 4A 4E DD 8E DB 02 42 22 D9 02 1B 34 44 24 12 7C 5E 63 DD D3 62
07 BC 0D 16 A9 94 E6 29 F4 A8 9D 7B 10 51 2D BC 88 6C E7 D5 5E 34 07 82 77 65
C2 DD B3 6F 61 02 9E 2B 2B |
4.7. (10 pts) As shown in
Table 4.1, the first several bytes of the ciphertext in case 2 and 3 are
identical (as highlighted), but the rest of the ciphertext in those two cases
were different. Explain the reason of this phenomenon. Hint: AES is a block
cipher.
Go to
the Index