|
T. Andrew Yang
|
last updated: 10/27/2022: Lab
2 posted 9/19/2022: projects posted 9/8/2022: first posted |
Total: 100
points
1.1.
(5 pts) Visit the class discussion group (link available in the
syllabus page). Post a message with your full name as the subject
line. In your post, briefly introduce yourself (including your full name) and
one item you most desire to learn in this class. Throughout this class, you
shall regularly participate at the discussion group to find recent
announcements, reminders, and discussions.
1.2. Answer the following questions. Cite your source(s).
Note: Not all information published on the web are
correct; discern the validity of the information you use.
1)
(5 pts) What is ubiquitous computing?
What is the relationship between ubiquitous
computing and mobile computing?
2)
(5
pts) What is the relationship between pervasive computing and wireless
computing?
3)
(5 pts) Some believe that
the Internet itself is a distributed system. Do you agree with this statement? Justify
your answer.
4)
(5
pts) What is the relationship between reliability and security of
a system?
5)
(5
pts) Explain what reliability
means. Is reliability related to failure
processing? Justify your answer.
6)
(5 pts) Explain what scalability means
in a distributed system. Give an example of a system or an algorithm that has
poor scalability.
7)
(10
pts) What is a middleware?
What is the role played by middleware in a distributed system?
1.3. Suppose John is using his laptop to send a piece of data (d) to Mary.
Below are some assumptions.
Assumptions:
(a) The IP of John’s laptop is John_IP, and its MAC/physical address is
John_MAC.
(b) Mary’s computer’s IP address is Mary_IP, and its MAC is Mary_MAC.
(c) The IP of the default gateway/router of John’s laptop is John_Router_IP,
and its MAC is John_Router_MAC.
Answer the following questions:
8)
(5 pts) How would the Layer-3 header (i.e., IP header) be
structured? Hint: Show the source address and the destination address.
9)
(5 pts) How would the Layer-2 header be structured? Hint: Show the
source address and the destination address.
10)
(5 pts) Explain how John’s default router would process the
packet sent from John’s computer.
1.4. Encapsulation vs Tunneling:
11)
(10 pts) What does encapsulation means in networking protocols? Give two examples of
tunneling protocols.
12)
(10 pts) What does tunneling means in networking protocols? Give two examples of
tunneling protocols.
1.5. Inter-process communication: Suppose process A has sent a message to
process B.
13)
(10 pts) When the communication is synchronous, what does that mean? Give
an example of synchronous communication.
14)
(10 pts) When the communication is asynchronous, what does that mean? Give
an example of asynchronous communication.
Go
to the Index
Total: 100 points
2.1 (10 pts) In Figure 4.6, the TCP server program uses two different sockets. One is
the ServerSocket class and the other is the Socket
class. Explain how those two different kinds of sockets are used by the TCP
server program.
2.2 (10 pts) The sockets abstraction may be implemented
as a UDP socket or a TCP socket. Explain the relative pros and cons of UDP
sockets and TCP sockets.
2.3 (10 pts) In Chapter 5
(Remote Invocation), it is said that RPC provides at least two types of
transparency: the location transparency and
the access transparency. First,
explain what each of those two means; secondly, explain whether one is implied
by the other. Justify your answer.
2.4 (20 pts) Suppose you’d
like to add location transparency to
the Request-Reply model as discussed in Chapter 5; that is, a client does not
need to specify the server’s specific location in order to send a request to
that server. Explain your design. Feel free to use a diagram to illustrate your
design. Provide sufficient detail about how the client and the servers would
communicate.
2.5 (10 pts) If a
communication paradigm is asynchronous,
is it also time-uncoupled? Explain
your answer with examples as appropriate.
2.6 (10 pts) If a
communication paradigm is synchronous,
is it also time-coupled? Explain your
answer with examples as appropriate.
2.7 (30 pts) Perform a
comparative study of message
passing and distributed shared memory (in chapter 6).
Would one of them be more efficient than the other? First, analyze the pros and
cons of each approach; then consider different application scenarios when
answering the given question.
Go
to the Index
NOTES:
(a)
This
can be an individual project or a two-person team project. Clearly indicate your team
status when submitting your project (on the top page of the documentation).
(b)
Each
person must submit the project, even if you are in a two-person team.
-
Objectives: This project provides hands-on experience
of developing distributed systems, in particular a system based on the service
brokerage pattern discussed in class. More discussions about brokers can be
found in the textbook, in particular Chapter 2 (System Architectures) and
Chapter 6 (Indirect Communication).
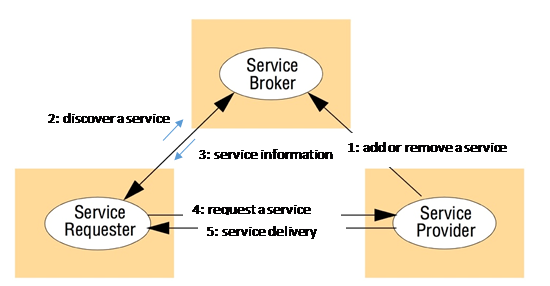
Figure 1. The Brokerage pattern
-
Description: As shown in Figure 1, there exist three types of entities in the system.
a)
A service provider provides services, which may be requested by
clients (that is, requesters).
b)
A service requester may request a service from a service provider.
c)
The service broker is in charge of keeping an inventory of
services published by service providers and, when requested by a service
requester, provides related service information in response to the request.
This project has two parts.
In part A, each team should develop the
following programs.
1)
The service broker:
§ The broker uses a well-known
port, which is to be used by both the service providers and the service
requesters when communicating with the service broker.
§ The broker should support
the service providers by allowing them to send addService( ) and
removeService( ) requests to the broker. The addService( ) request from
a service provider causes the broker to add the name of the service, the IP
address of the provider, and the port number to be used for that service. The removeService(
) request causes the broker to find and remove the named service from its
directory of services.
§ The broker should support
the service requesters by allowing them to send discoverService( )
requests, which include a key phrase of the requested service. The broker
should look up services in the service directory using the specified key
phrase, and return the service provider that best matches that key phrase; if
no matching service is found, it returns an error code to the requester.
2)
Service provider #1: The randomNumberGenerator provider supplies a
random number to the requester.
3)
Service provider #2: The hashGenerator provider takes a string
(for example, “How are you doing?”) and the name of a hash method (for example,
MD5) as the input from the client and returns the hash value generated from the
given string using the specified hash method. The string “How are you doing?”,
for instance, will be hashed into the hash value
“60F4A68C292CF0E697C9E65057DCB5B4” (in hexadecimal). Use the online hash
calculator at https://www.pelock.com/products/hash-calculator
to verify the hash value produced by your hashGenerator provider.
Both providers
must request the service broker to add their services to the directory, via the
addService( ) request. They may remove their respected services from the
directory by sending the removeService( ) request to the broker.
4)
The client (i.e., service requester) should provide an
appropriate user interface allowing the user to specify or choose what the user
would want the client program to do; this user input process should continue until
the user chooses to exit from the program.
a.
If the user chooses to get a hash value for a given string using the
chosen hashing method, the service requester will first send a discoverService(
) request to the broker in order to find the IP and port# of the service
provider; it then sends a message to the provider (with the source string and
the hash method as the input parameters) and, in return, gets the hash value
back from the provider. Once the hash value is available, the requester then
displays it on the user screen.
b.
If the user chooses to get a random number, the service requester will
first send a discoverService( ) request to the broker in order to find the IP
and port# of the service provider; it then sends a message to the provider and,
in return, gets a random number back from the provider. Once the random number
is available, the requester then displays it on the user screen.
c.
If the user’s request cannot be handled, the requester should print
appropriate error messages on the user screen.
In part B of the project, each team should
revise the programs from part A by adding the following enhancements.
1)
The service broker will authenticate the provider first before adding the
requested service to the directory. For example, the broker may require a
provider to register itself first with the broker, with an id and password. If
password-based authentication is used to authenticate the provider, the
addService( ) and the removeService( ) requests may need to include the
provider’s id and password as part of the parameters.
2)
(Bonus, 20% more) In addition to the
password-based authentication, you may implement two-factor authentication.
That is, in addition to the id and password, the broker may send a one-time
code to the requesting provider and require the provider to include that
one-time code when requesting to add a service or remove a service.
-
To hand in:
a)
Part A
specification:
Clearly specify
the communication protocols between the entities, including those between the
broker and the provider, between the broker and the requester, and between the
requester and the provider.
b)
Part A complete programs:
Include the
design documents and the complete source programs in a single zip file, and
submit the zip file in Blackboard.
Give the TA a
demo of your running program. The demo should be completed within a week
after the due date.
c)
Part B complete programs:
Include the
design documents and the complete source programs in a single zip file, and
submit the zip file in Blackboard.
Give the TA a demo of your
running program. The demo should be completed within a week after the due
date.
Go to the Index