 Examples Overview >
Examples Overview >
 Small Project Development Case >
Small Project Development Case >
 Project Lifecycle >
Project Lifecycle >
 Inception
Inception
 Examples Overview >
Examples Overview >
 Small Project Development Case >
Small Project Development Case >
 Project Lifecycle >
Project Lifecycle >
 Inception
Inception
|
|
Table of Contents |
Topics (on this page) |
This illustration shows how the first iteration of a small project might be planned. The lengths of the bars in the chart (indicating duration) have no absolute significance. There is also no intention to suggest the application of a uniform level of effort across the duration of the workflows. You can navigate to the corresponding task description from each line of the chart - just click on the task name. This illustration was created from a Microsoft Project Plan.
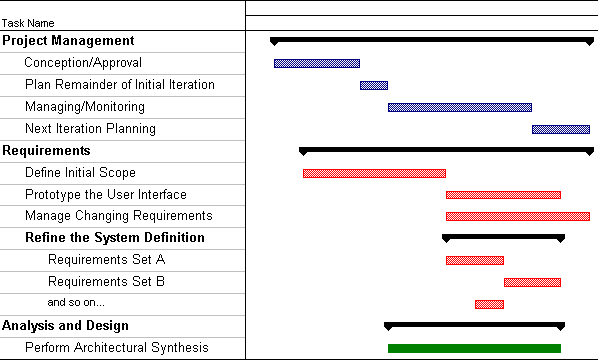
| Task | Description |
| Project Management: | |
| Conception/Approval |
This includes the workflow details: The main output artifacts are:
A more detailed plan would include some review milestones. |
|
This includes workflow details: The principal output artifact is: |
|
| Managing/Monitoring |
This represents ongoing project management activities, including the following workflow details: The principal output artifacts are: |
|
This includes workflow details:
The principal output artifacts are:
The results of status assessments and iteration assessments should be considered in determining if any changes to process and tools are necessary. |
|
| Requirements | |
|
Define Initial Scope |
This includes the workflow details:
|
|
This includes the Activity: Prototype the User Interface. The main output artifact is User-Interface Prototype. |
|
|
This tasks tracks effort related to managing changes to requirements described in the initial Vision (as baselined at the end of the task Define Initial Scope). The relevant workflow detail is: Manage Changing Requirements. |
|
|
This includes the workflow detail Refine the System Definition (except for user-interface related activities, which are a separate task). The main output artifacts are:
The effort to define requirements is divided into smaller tasks with shorter durations (around 1 week is typical). These are represented in the example plan as "Requirements Set A", "Requirements Set B", and so on. Tasks are typically organized around use cases or scenarios, with other tasks to detail supplemental requirements or investigate specific issues or risks. |
| Analysis and Design | |
|
Perform Architectural Synthesis |
If the risks are judged to be high, then it may be necessary to do more exploration in this initial inception phase iteration. This workflow detail is: The main output artifact is an Architectural Proof-of-Concept. |
Configuration Management tasks (workflow details: Change and Deliver Configuration Items and Manage Change Requests) are folded into the above tasks. Administrative and environment support tasks have been omitted for simplification.
The scope of the project should be understood, and the stakeholders initiating the project should have a good understanding of the project's ROI (return on investment), i.e. what is returned, for what investment cost. Given this knowledge, a go/no go decision can be taken.
In cases where the project involves new product roll-out or creation of new technology, subsequent iterations may be needed to further define the scope of the project, the risks and the benefits. This may involve further enhancing the use-case model, business case, risk list, architectural proof-of-concept, or project and iteration plans. Extension of the Inception phase may also be advisable in cases where both the risk and the investment required are high, or where the problem domain is new or the team inexperienced.
|
Rational Unified
Process
|